Human-Machine Interface (HMI) systems have evolved significantly over the past few decades, driven by the need for more intuitive and efficient user interactions in industrial settings. The role of advanced graphics in enhancing HMI performance cannot be overstated. By leveraging modern graphical technologies, developers can create interfaces that are not only more visually appealing but also more functional and user-friendly.
The Importance of Advanced Graphics in HMI
Advanced graphics play a crucial role in the effectiveness of HMIs. They improve the clarity of information, reduce the cognitive load on operators, and facilitate quicker decision-making. Traditional text-based and rudimentary graphical interfaces often fall short in providing the level of detail and intuitiveness required in complex industrial environments.
Improving Clarity and Readability
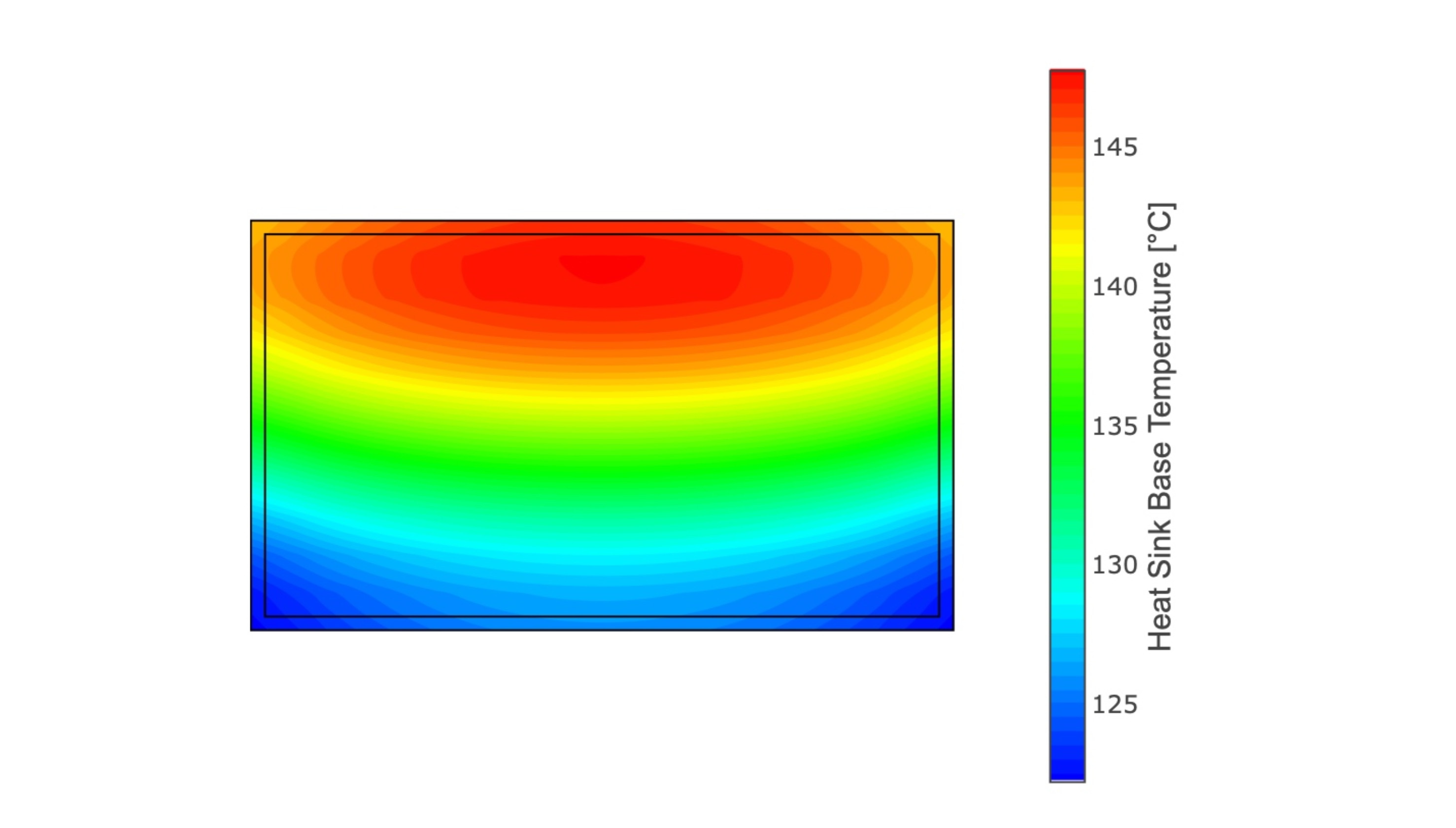
One of the primary benefits of advanced graphics is the enhancement of clarity and readability. High-resolution displays and sophisticated graphic design enable the presentation of information in a more organized and visually digestible manner. For instance, using color-coded visuals, 3D models, and detailed schematics can help operators quickly identify issues and understand the state of a system at a glance.
Reducing Cognitive Load
Cognitive load refers to the amount of mental effort required to process information. In an industrial setting, where operators are often inundated with vast amounts of data, reducing cognitive load is essential. Advanced graphics help in this regard by presenting information in a more intuitive way. Visual cues, animations, and dynamic displays can guide the operator's attention to critical areas, making it easier to monitor and control processes without being overwhelmed by data.
Facilitating Quick Decision-Making
The ability to make quick and informed decisions is critical in many industrial environments. Advanced graphics can significantly speed up the decision-making process by providing real-time data visualization and interactive controls. For example, a well-designed HMI can highlight anomalies or deviations from the norm using visual alerts, allowing operators to take immediate corrective actions.
Technologies Enabling Advanced Graphics
Several technologies are driving the advancement of graphics in HMI systems. From sophisticated rendering engines to augmented reality (AR), these technologies are transforming how operators interact with machines and systems.
High-Resolution Displays
High-resolution displays are a fundamental component of modern HMIs. They offer greater detail and clarity, allowing for more complex and detailed visualizations. With the advent of 4K and even 8K displays, HMIs can now provide incredibly sharp and detailed graphics, which are essential for tasks that require precision.
GPU Acceleration
Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) have revolutionized the rendering of complex graphics. By offloading graphic processing tasks from the CPU, GPUs enable smoother animations, real-time data visualization, and the handling of more sophisticated graphical elements without lag. This capability is particularly important for HMIs that require real-time updates and responsiveness.
Vector Graphics
Vector graphics, unlike raster graphics, use mathematical equations to represent images. This allows them to be scaled to any size without losing quality, making them ideal for HMIs that need to display graphics on different screen sizes and resolutions. Vector graphics are also typically more efficient to render, which can improve overall system performance.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality (AR) is an emerging technology that overlays digital information onto the physical world. In the context of HMIs, AR can provide operators with additional layers of information directly in their field of view. For example, an AR-enabled HMI can display maintenance instructions or highlight critical system components, enhancing situational awareness and efficiency.
Designing Effective HMI Graphics
Creating effective HMI graphics involves a careful balance of aesthetics and functionality. The goal is to design interfaces that are not only visually appealing but also enhance usability and performance.
Prioritizing Usability
Usability should always be the primary consideration in HMI design. This means creating interfaces that are intuitive and easy to navigate. Consistency in design elements, such as buttons, icons, and menus, helps users quickly learn and navigate the system. Additionally, ensuring that important information is easily accessible and not buried under multiple layers of menus can significantly improve usability.
Using Color Wisely
Color is a powerful tool in HMI design. It can convey information quickly and effectively, but it must be used judiciously. Overuse of color can lead to clutter and confusion. Instead, use color to highlight critical information, indicate status changes, and guide the operator's attention. For example, red might be used for alarms and warnings, while green could indicate normal operation.
Incorporating Animations
Animations can enhance the user experience by providing visual feedback and aiding in the understanding of complex processes. For instance, animations can be used to demonstrate how different parts of a system interact or to show the progression of a process in real-time. However, it's important to use animations sparingly and ensure they do not distract or overwhelm the user.
Ensuring Responsiveness
In an industrial setting, HMIs must be highly responsive. Delays in the display of information or the response to user inputs can lead to inefficiencies and even safety hazards. Advanced graphics should be optimized for performance to ensure that the interface remains responsive even under heavy loads.
Case Studies in Advanced HMI Graphics
Several industries have successfully implemented advanced graphics in their HMIs, leading to significant improvements in performance and user satisfaction.
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, advanced graphics have been used to create more intuitive and effective HMIs for monitoring and controlling production lines. For example, detailed 3D models of machinery allow operators to better understand the status and condition of equipment. Real-time data visualizations help in identifying and addressing issues promptly, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency.
Energy
The energy sector has also benefited from advanced HMI graphics. In power plants and grid management systems, high-resolution displays and real-time data visualization are crucial for monitoring complex systems. Advanced graphics enable operators to quickly assess the state of the system, identify potential issues, and take corrective actions, thereby ensuring the reliable delivery of energy.
Healthcare
In healthcare, advanced HMIs are used in various applications, from medical imaging to patient monitoring systems. High-resolution displays and intuitive graphical interfaces help healthcare professionals to diagnose and monitor patients more effectively. For example, advanced imaging systems provide detailed visualizations of medical scans, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Future Trends in HMI Graphics
The future of HMI graphics is promising, with several emerging trends set to further enhance performance and user experience.
Increased Use of AR and VR
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are expected to play a more significant role in HMIs. These technologies can provide immersive experiences that offer new ways to interact with complex systems. For example, VR can be used for training purposes, allowing operators to practice handling different scenarios in a safe, virtual environment.
AI-Driven Graphics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize HMI graphics. AI can be used to analyze user interactions and optimize the interface in real-time, providing a more personalized and efficient user experience. Additionally, AI-driven analytics can help in predicting and preventing issues, further enhancing the reliability and performance of HMI systems.
Touchless Interfaces
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the development of touchless interfaces. These interfaces use technologies such as gesture recognition and voice control to interact with the HMI, reducing the need for physical contact. Touchless interfaces can enhance hygiene and reduce the spread of pathogens, making them particularly valuable in healthcare and food processing industries.
Conclusion
The integration of advanced graphics in HMI systems represents a significant leap forward in enhancing performance, usability, and user satisfaction. By leveraging high-resolution displays, GPU acceleration, vector graphics, and emerging technologies like AR, developers can create HMIs that are not only more visually appealing but also more functional and efficient. As these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect even greater advancements in HMI performance, paving the way for more intuitive and effective human-machine interactions.
In summary, the future of HMI is bright, with advanced graphics leading the charge towards more sophisticated, user-friendly, and responsive interfaces. By prioritizing usability, optimizing performance, and embracing new technologies, we can create HMIs that truly enhance the human experience in industrial environments.